Themes of the 2026 Edition
Additive Manufacturing
Redefining production through layer-by-layer innovation
Additive manufacturing (AM), commonly referred to as 3D printing, is a transformative approach to production that builds components layer by layer directly from digital models. Unlike subtractive methods, AM enables complex geometries, lightweight structures, and rapid prototyping without the need for extensive tooling. This technology is being increasingly applied across many industrial sectors to achieve design freedom, material efficiency, and customization. In this conference, the emphasis will be placed on:
Additive manufacturing (AM), commonly referred to as 3D printing, is a transformative approach to production that builds components layer by layer directly from digital models. Unlike subtractive methods, AM enables complex geometries, lightweight structures, and rapid prototyping without the need for extensive tooling. This technology is being increasingly applied across many industrial sectors to achieve design freedom, material efficiency, and customization. In this conference, the emphasis will be placed on:
Feedstock production and procurement
Design for additive manufacturing
Printing processes and finishing technologies
Non-destructive inspection and testing
Qualification and certification strategies

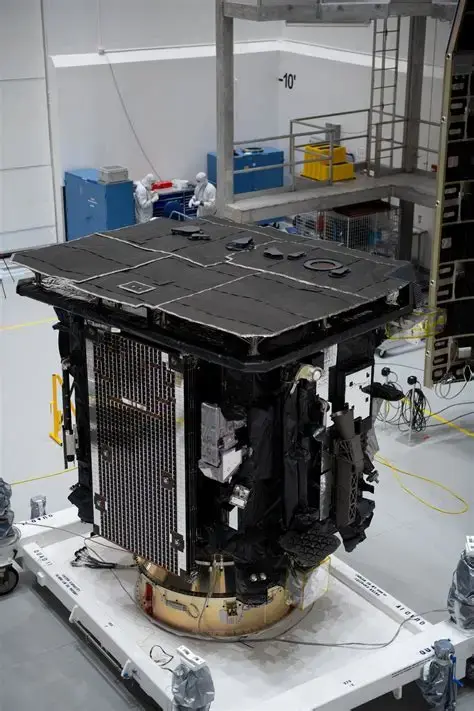
Caption: Additivelly manufactured Upper Stage Elecro Valve Box
Credit: Thales Alenia Space, LAMBDA-X, Safran, SCL, 3D systems
Joining Technologies
Advanced methods to connect materials and enable complex assemblies.
Joining technologies encompass the processes used to connect materials and components, enabling structural integrity and functionality in complex assemblies. Methods range from traditional welding, brazing, and soldering to advanced techniques such as friction stir welding, laser joining, and adhesive bonding. The technology to be employed depends on factors such as material type, mechanical requirements, service environment, and manufacturability. Innovations in joining aim to accommodate advanced alloys, composites, and dissimilar materials, addressing challenges of thermal stress, residual distortion, and long-term reliability. In this conference, the main topics of interest are:
Joining technologies encompass the processes used to connect materials and components, enabling structural integrity and functionality in complex assemblies. Methods range from traditional welding, brazing, and soldering to advanced techniques such as friction stir welding, laser joining, and adhesive bonding. The technology to be employed depends on factors such as material type, mechanical requirements, service environment, and manufacturability. Innovations in joining aim to accommodate advanced alloys, composites, and dissimilar materials, addressing challenges of thermal stress, residual distortion, and long-term reliability. In this conference, the main topics of interest are:
Arc, power beam, and solid-state welding
Adhesive bonding and mechanical fastening
Hybrid joining methods
Joining of dissimilar materials

Caption: Using Linear Friction Welding to add connection tabs onto fuel tank domes to reduce raw material costs
Credit: TWI Ltd, Airbus Defence and Space.
Composite Manufacturing
Composite manufacturing encompasses the design of innovative material systems, the fabrication of advanced structural solutions and the application of state-of-the-art characterisation and modelling techniques. By exploring diverse reinforcements and matrices, it aims to deliver high specific strength, tailored properties and optimised designs. Processes such as resin transfer moulding, automated fibre placement, filament winding and tape placement approaches are central to fabricating advanced composite parts. These methods enable light, yet durable structures used in a variety of applications, from aerospace and automotive to wind energy and sporting goods. Topics of interest include:
Polymer based composites (thermoset and thermoplastic)
Automated fibre placement and lay-up techniques
Curing, forming and consolidation processes
Metallic and ceramic matrix composites
Testing, inspection and repair of composite structures
Advanced modelling of composite materials

Credit: Airbus Defence and Space
Surface Engineering
Tailoring surfaces to enhance durability, function, and efficiency.
Surface engineering involves modifying the outermost layers of materials to enhance properties such as wear resistance, corrosion protection, thermal stability, and biocompatibility. Common techniques include coatings, thermal spraying, chemical treatments, ion implantation, and laser surface modification. By tailoring surface characteristics without altering bulk material properties, engineers achieve extended service life and improved performance under demanding conditions. Applications span aerospace, energy, biomedical implants, and industrial machinery, where environmental and operational stresses are severe. In this conference, the topics of interest include:
Surface engineering involves modifying the outermost layers of materials to enhance properties such as wear resistance, corrosion protection, thermal stability, and biocompatibility. Common techniques include coatings, thermal spraying, chemical treatments, ion implantation, and laser surface modification. By tailoring surface characteristics without altering bulk material properties, engineers achieve extended service life and improved performance under demanding conditions. Applications span aerospace, energy, biomedical implants, and industrial machinery, where environmental and operational stresses are severe. In this conference, the topics of interest include:
Corrosion protection systems and coatings
Surface preparation and cleaning methods
Advanced surface treatments (e.g. laser or mechanical peening)
Functional coatings for thermal, electrical or optical performance

Caption: Coated heat shield used by Solar Orbiter which helps protect it against overheating in the harsh conditions close to the Sun.
Credit: ESA
Electronic Materials and Processes
The foundation of modern devices, from semiconductors to quantum systems.
Electronic materials and processes encompass the specialized substances and fabrication methods required to build modern electronic devices. Key materials include semiconductors, dielectrics, conductors, and emerging options such as organic electronics and 2D materials. Fabrication processes—such as lithography, deposition, etching, and packaging—demand nanoscale precision and defect control. Ongoing research focuses on scaling performance, enhancing energy efficiency, and enabling new device architectures for computing, sensing, and communications. In the context of this conference, the topics of interest include:
Electronic materials and processes encompass the specialized substances and fabrication methods required to build modern electronic devices. Key materials include semiconductors, dielectrics, conductors, and emerging options such as organic electronics and 2D materials. Fabrication processes—such as lithography, deposition, etching, and packaging—demand nanoscale precision and defect control. Ongoing research focuses on scaling performance, enhancing energy efficiency, and enabling new device architectures for computing, sensing, and communications. In the context of this conference, the topics of interest include:
Printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing and high-density interconnects
Additive and semi-additive electronics fabrication
Green electronics (lead-free, solderless technologies)
Modelling, simulation, and reliability assessment
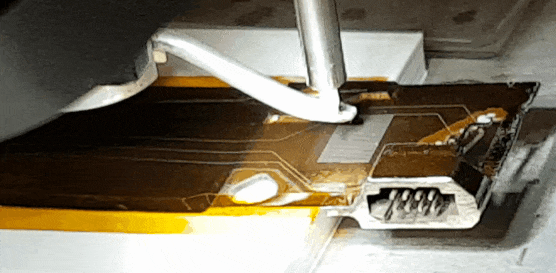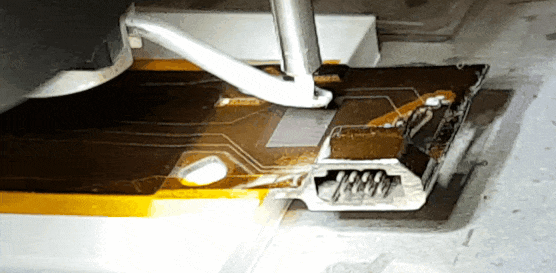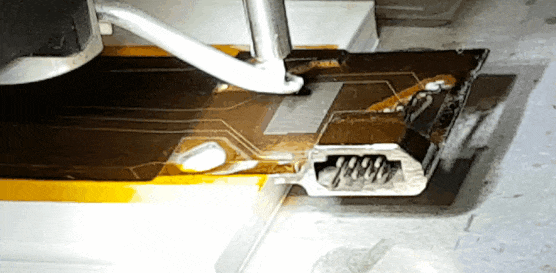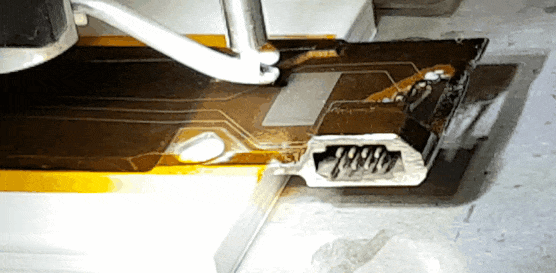
Credit: CSEM